By transforming raw data into vector embeddings, you've unlocked a wealth of potential. These vectors encapsulate the essence of your data, but their full value isn't realized until you apply them in your Vector Search & Management.
Vector Search & Management is the bridge between the latent, abstract mathematical representations of your data and their real-world applications. Your Vector Management stores, structures, and prepares your vector data for various machine learning tasks. Using Vector Search, you can perform efficient and relevant data retrieval from extensive data repositories.
Vector Search & Management empower critical objectives:
Quality Evaluation: Application success depends on your vector quality. You can use Vector Search to thoroughly assess and fine-tune the performance of embeddings of all types, including word, image, document, product, music & audio, face, tag, and features (in ML).
Model Training: Vector representations are essential for training models in multiple domains, including transfer learning (e.g., language translation, image style transfer), reinforcement learning (autonomous driving, robotic control), content-based recommendation systems (e-commerce, music), anomaly detection (manufacturing quality control, network anomaly detection), active learning (image classification, text sentiment analysis), and embedding space analysis (document clustering, user behavior profiling).
Real-Time Retrieval: In live systems, Vector Search is the foundation for real-time retrieval, powering functions like visual similarity search in online image search engines, streaming platforms as well as video, music, and article suggestions on news sites, content tagging and classification on, e.g., social media sites, online reverse image search, and voice search in voice assistants and search engines.
How you use your Vector Search & Management to achieve these objectives depends on your use case requirements and constraints, where it fits in terms of a few Core Parameters, how you tailor Nearest Neighbor Search, and which Key Access Patterns you utilize.
Let’s look at each of these below.
To understand Vector Search & Management and their role in retrieval systems, we need to explore the key requirements that shape their implementation. These requirements vary with the specific use cases and tasks the retrieval system aims to accomplish.
Let's break down the retrieval system’s key defining parameters:
Update Frequency: Vectors can remain static over time or undergo frequent updates. In many retrieval systems, vectors are used to represent evolving data that requires regular refreshing. For example, on e-commerce platforms, product recommendations must adapt as new products are added, and customer preferences change.
In contrast, in a static library of scientific articles, vector updates happen less frequently. The frequency at which the vectors change crucially affects how they are managed and accessed.
Access Patterns: Access patterns – how vectors are queried and retrieved within the retrieval system – can vary widely, ranging from real-time, on-the-fly, queries for nearest neighbors of single vectors, to batch processing and integration with other data. Emergency response systems (e.g., 911 dispatch), for instance, rely on quick access real-time similarity searches to find the closest available emergency responders to a reported incident location. Here, low-latency access can mean the difference between life and death.
Whereas, a video processing pipeline handling large sets of video frames for analysis will mainly focus on batch processing. Access patterns play a critical role in determining the efficiency of vector retrieval, and, therefore, whether real-time or batch processing is preferred.
Priorities: The priorities of your particular application determine what matters most: minimizing latency, maximizing throughput, or ensuring a high level of accuracy. For example, low-latency access to real-time data is paramount for making split-second decisions in a financial trading system. In contrast, a data analytics platform might prioritize high throughput to process large volumes of data quickly.
What you choose to prioritize affects your retrieval system's architecture and the trade-offs made during implementation.
An efficient and effective Vector Search & Management approach must carefully consider and quantify the retrieval system’s update frequency, access patterns, and priorities to meet the requirements of the intended use case, whether it’s providing instant e-commerce product recommendations, facilitating real-time decision-making, conducting in-depth data analysis, or something else entirely.
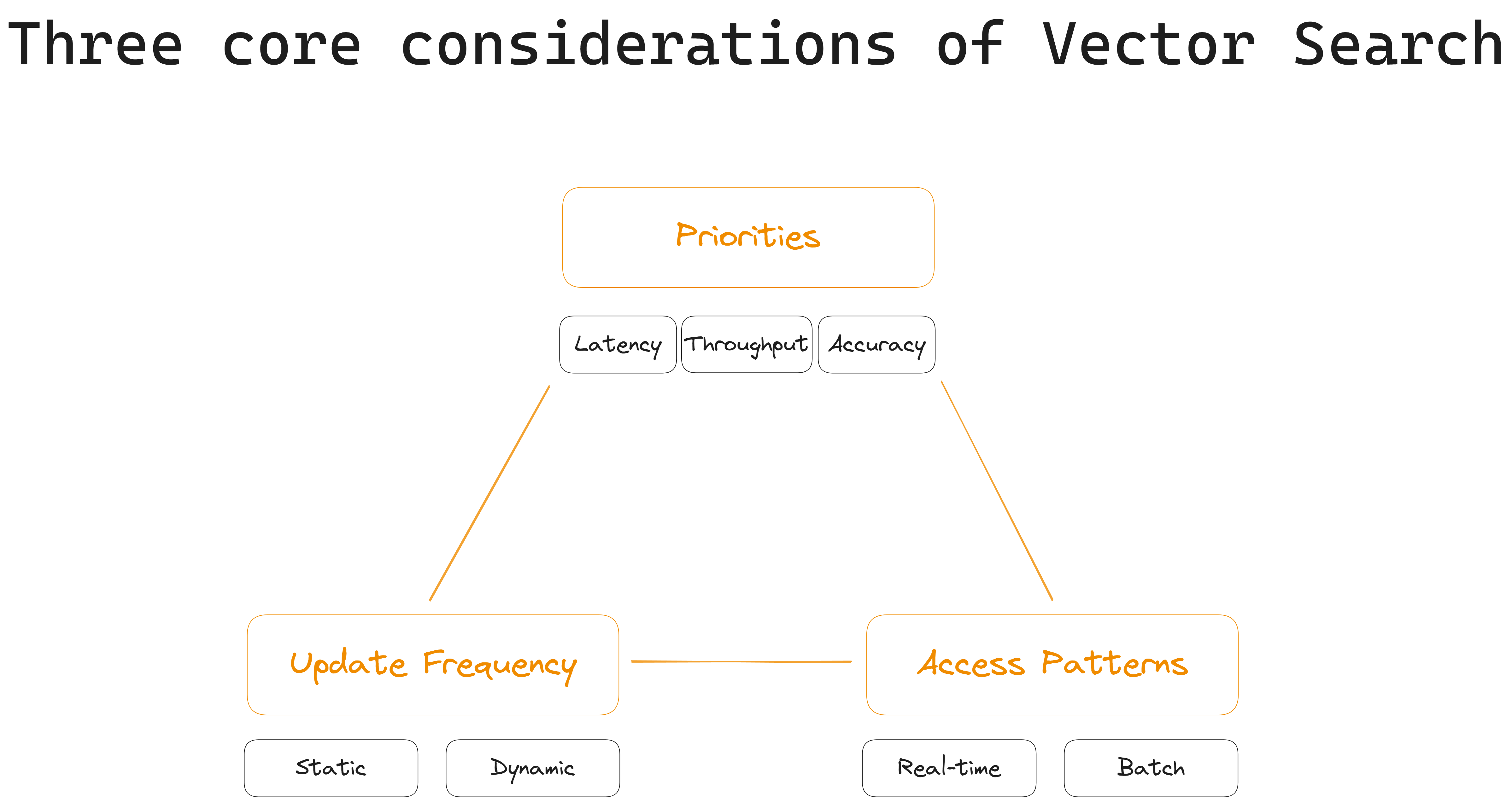
The above visual's key takeaway: Our three corners (priorities, update frequency, access patterns) interact to determine the design of our system. Depending on our project, we may privilege one or two corners over the other/s. For example, if we're building a recommendation system for an online store, we would emphasize "real-time" interactions and "speed" to offer customers instant, personalized recommendations.
Now let's dive into the details.
Scanning to calculate the similarity between vectors quickly is at the heart of Vector Search. Vector similarity scores encoded by your embedding model/s store valuable feature or characteristic information about your data that can be used in various applications (e.g., content recommendation, clustering, data analysis). There are several ways to perform nearest neighbor search.
Read more about different vector search algorithms, here
The access patterns deployed in Vector Search significantly impact storage, query efficiency, and infrastructure alignment, which are consequential in optimizing your retrieval system for your intended application.
Read more about the different access patterns, here
So what does this all mean?
Read our conclusions and recommended next steps, here
Stay updated with VectorHub